views
Series Circuit
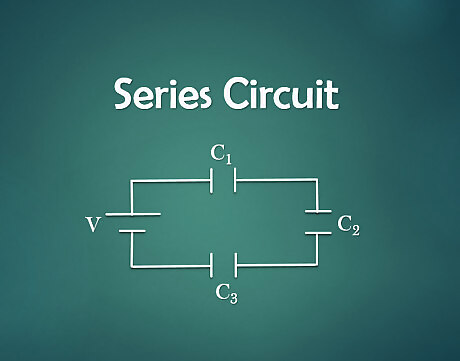
Identify the circuit. A series circuit has only one loop with no branching paths. Capacitors in the circuit are arranged in order within the same loop.
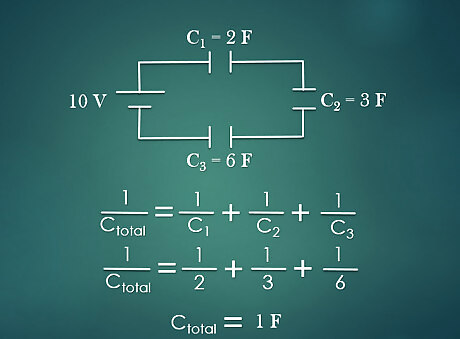
Calculate the total capacitance. Given the voltage and capacitor values for each, find the total capacitance. To calculate the total capacitance in a series circuit, use the formula 1 C T = 1 C 1 + 1 C 2 + 1 C 3 {\displaystyle {\frac {1}{C_{T}}}={\frac {1}{C_{1}}}+{\frac {1}{C_{2}}}+{\frac {1}{C_{3}}}} {\frac {1}{C_{T}}}={\frac {1}{C_{1}}}+{\frac {1}{C_{2}}}+{\frac {1}{C_{3}}}. For example: A series circuit has three different capacitors of value C1 = 2F, C2 = 3F, C3 = 6F. Plug in to the formula 1 C T = 1 2 + 1 3 + 1 6 {\displaystyle {\frac {1}{C_{T}}}={\frac {1}{2}}+{\frac {1}{3}}+{\frac {1}{6}}} {\frac {1}{C_{T}}}={\frac {1}{2}}+{\frac {1}{3}}+{\frac {1}{6}} and solve for CT. Adding the fraction and taking the inverse, CT = 1F.
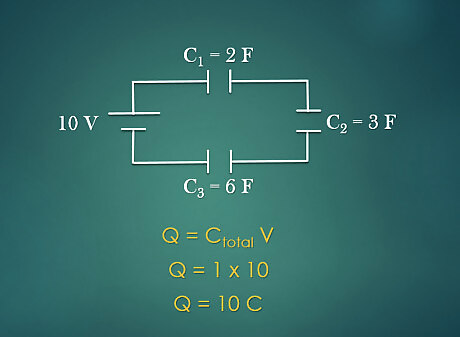
Calculate the total charge. The total charge in a circuit depends on the total voltage and the total capacitance in a circuit. This relationship is given by the equation Q = C V {\displaystyle Q=CV} Q=CV. For example: The circuit has a total capacitance of 1 F and total voltage of 10 V. Plug in the given to the equation and solve for Q: Q = 1 ∗ 10 = 10 C {\displaystyle Q=1*10=10C} Q=1*10=10C
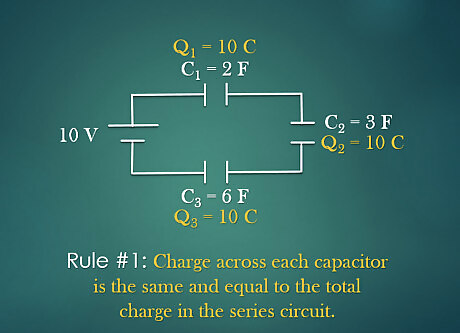
Find the charge in each capacitor. For a series circuit, charge across each capacitor is the same and equal to the total charge in the circuit. For example: The total charge in the circuit is 10 C. Then the charge in C1 is 10 C, C2 is 10 C and C1 is 10C.
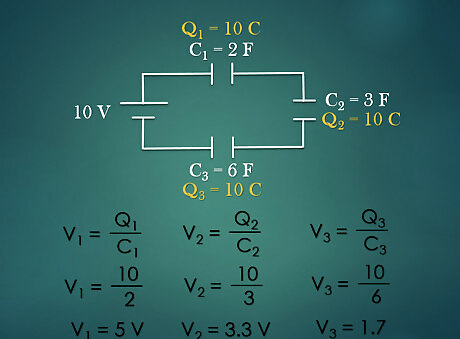
Calculate the voltage across each capacitor. Rearranging the equation Q = C V {\displaystyle Q=CV} Q=CV to V = Q / C {\displaystyle V=Q/C} V=Q/C, the voltage across each capacitor can be calculated. For Example: The charge is 10 C for all capacitors and capacitance values are 2 F, 3 F and 6 F respectively. Voltage across first capacitor is V1 = Q1/C1 = 10/2 = 5V Voltage across second capacitor is V2 = Q2/C2 = 10/3 = 3.3V Voltage across third capacitor is V3 = Q3/C3 = 10/6 = 1.7 V Note that the sum of individual voltage equals the total voltage in the series circuit.
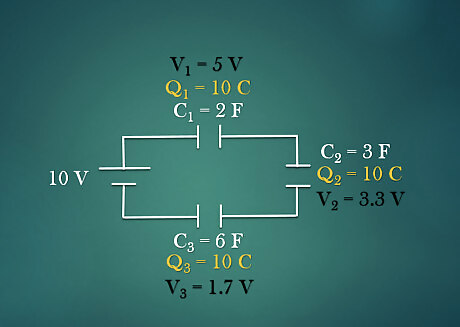
Draw and label each capacitor with its charge and voltage. Once the voltage and charge in each capacitor is calculated, the circuit is solved. Label these information in the circuit drawing to keep everything organized. .
Parallel Circuit
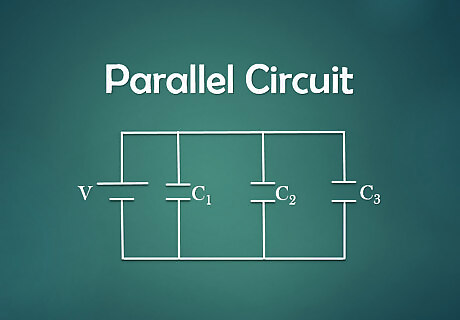
Identify the circuit. A parallel circuit has more than one loop and all are connected to same voltage. The capacitors in the circuit are arrange in parallel to each other.
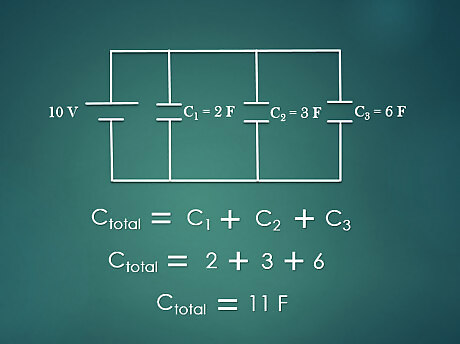
Calculate the total capacitance. The sum of all the capacitance value in a parallel circuit equals to the total capacitance in the circuit. This is given by the equation CT=C1+C2+C3. . For example: A parallel circuit has three capacitors of value: C1 = 2F, C2 = 3F, C3 = 6F. Then the total capacitance, CT is 2+3+6 = 11 F.
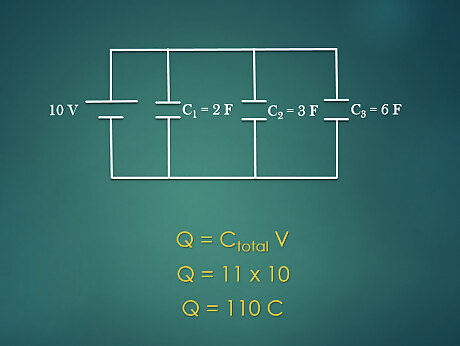
Calculate the total charge. The total charge in a circuit depends on the total voltage and the total capacitance in a circuit. This relationship is given by the equation Q = C V {\displaystyle Q=CV} Q=CV. For example: The circuit has a total capacitance of 11 F and total voltage of 10 V. Plug in the givens to the equation: Q = 11*10 = 110 C.
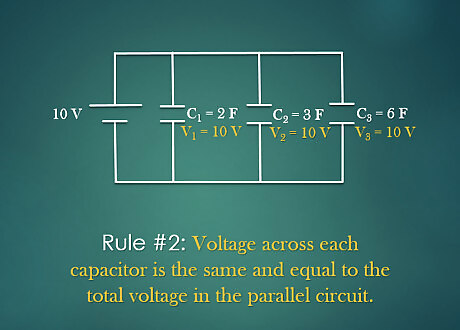
Find the total voltage across each capacitor. In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each capacitor is the same and equal to the total voltage in the circuit. For example: The total voltage in the circuit is 10 V. Then the voltage across V1 is 10 V, V2 is 10 V and V3 is 10 V.
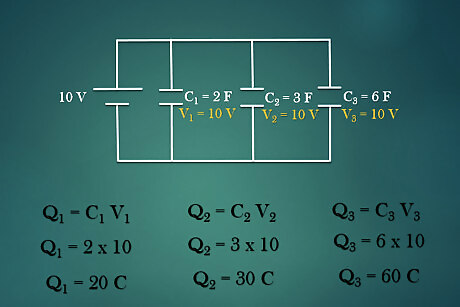
Calculate the charge in each capacitor. Once the voltage is identified for each capacitor with a known capacitance value, the charge in each capacitor can be found using the equation Q = C V {\displaystyle Q=CV} Q=CV. For example: The voltage across all the capacitors is 10V and the capacitance value are 2F, 3F and 6F respectively. Charge in first capacitor is Q1 = C1*V1 = 2*10 = 20 C. Charge in first capacitor is Q2 = C2*V2 = 3*10 = 30 C. Charge in first capacitor is Q3 = C3*V3 = 6*10 = 60 C.
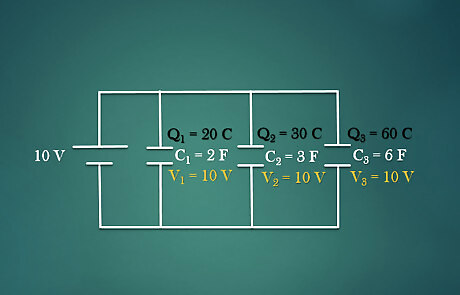
Draw and label each capacitor with its charge and voltage. Once the voltage and charge in each capacitor is calculated, the circuit is solved. Label these information in the circuit drawing to keep everything organized.
















Comments
0 comment