views
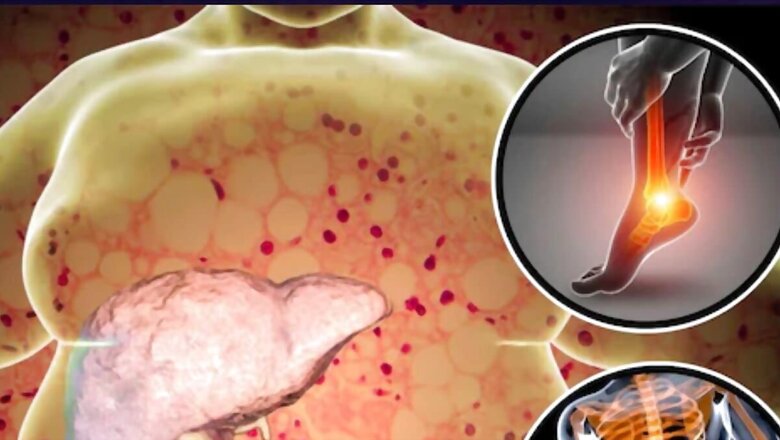
Hepatomegaly (enlarged liver) and fatty liver disease (steatosis) are conditions with various overlapping causes and risk factors. Here’s an in-depth look at the specific causes:
Fatty Liver Disease (Steatosis)
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is characterized by an excessive accumulation of fat in the liver cells. It can be classified into two main types:
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD):Cause: Chronic and excessive alcohol consumption is the primary cause. Alcohol metabolism in the liver produces toxic byproducts that damage liver cells, leading to fat accumulation.
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):Cause: The exact cause is not completely understood, but it is closely associated with metabolic syndrome, which includes conditions such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia. NAFLD can further progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), characterized by liver inflammation and damage.
- Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD)Previously known as NAFLD, MAFLD is more descriptive of the metabolic dysfunction underlying the disease. It is strongly linked to:Obesity: Excess body fat, especially visceral fat, is a significant risk factor.
- Type 2 Diabetes MellitusInsulin resistance leads to increased fat storage in the liver.Dyslipidemia: Elevated levels of triglycerides and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol contribute to liver fat accumulation.Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity is associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome, increasing the risk of MAFLD.
- Unhealthy DietDiets high in refined sugars, saturated fats, and trans fats contribute to fat buildup in the liver.
- HepatomegalyHepatomegaly is an enlargement of the liver and can result from various underlying conditions, including:
Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD and MAFLD):
Excessive fat accumulation can cause the liver to enlarge.
Liver Infections:
- HepatitisViral hepatitis (Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E) can cause liver inflammation and enlargement.
- Other InfectionsBacterial, parasitic, and fungal infections can also lead to hepatomegaly.Liver Tumors:
- Benign TumorsSuch as hepatic adenomas and hemangiomas.
- Malignant TumorsPrimary liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma) and metastatic cancers.
Metabolic Disorders:
Hemochromatosis
Excess iron deposition in the liver.
Wilson’s Disease
Excess copper accumulation.
Heart Failure:
Congestive heart failure can lead to liver congestion and enlargement due to blood backing up in the liver.
Infiltrative Diseases:
Amyloidosis: Abnormal protein deposits in the liver.
Glycogen Storage Diseases: Excessive glycogen storage due to enzyme deficiencies.
Prevention and Management
To prevent and manage fatty liver disease and hepatomegaly, consider the following lifestyle modifications:
- Weight LossAchieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
- Healthy DietConsuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats while avoiding excessive sugar and alcohol.
- ExerciseEngaging in regular physical activity to improve overall metabolic health.
- Medical ManagementRegular monitoring and management of diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.
- Avoiding ToxinsLimiting alcohol consumption and avoiding unnecessary medications and toxins that can harm the liver.Early detection and intervention are crucial to preventing the progression of fatty liver disease to more severe liver conditions, such as cirrhosis and liver cancer. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers, liver function tests, and imaging studies like fibroscan can help monitor liver health and guide treat

















Comments
0 comment