views
Creating a File
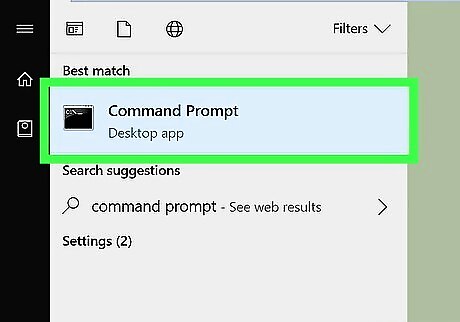
Open the Command Prompt. The easiest way to do this is to press Win + S to activate the search bar, type cmd, and then click Command Prompt in the search results.
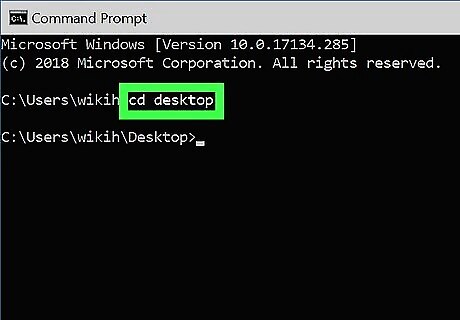
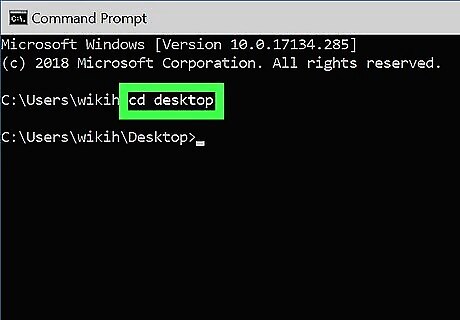
Go to the directory in which you want to create the file. The prompt will open to C:\Users\YourName by default. If the directory is somewhere else, type cd path_to_directory and press Enter. Replace path_to_directory with the actual directory location. For example, if you want to create a file on the Desktop, type cd desktop and press Enter. If the directory you're looking for isn't in your user directory (e.g., C:\Users\YourName), you'll have to type in the whole path (e.g., C:\Users\SomeoneElse\Desktop\Files).
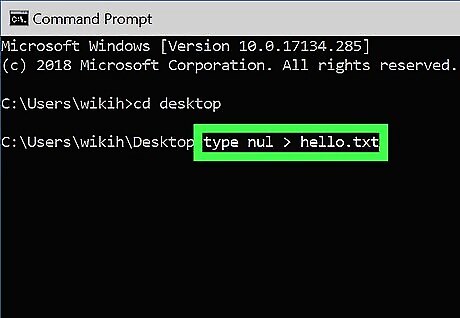
Create an empty file. If you don't want to create an empty file, skip to the next step. To create an empty file: Type type nul > filename.txt. Replace filename.txt with whatever you want to call your new file. The ".txt" part indicates that this is a plain text file. Other common file extensions include ".docx" (Word document), ".png" (empty photo),and ".rtf" (rich text document). All of these file types can be read on any Windows computer without installing additional software. Press Enter.
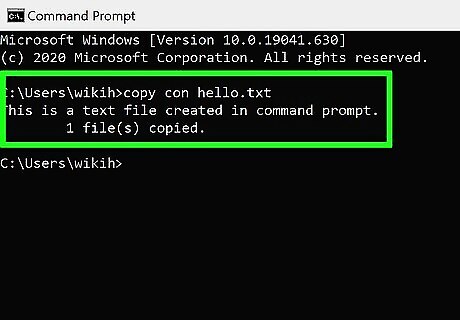
Create a file containing certain text. If you don't want to create a file with certain text inside, skip to the next step. Use these steps to create a plain text file that you can type into: Type copy con testfile.txt, but replace testfile with the desired file name. Press Enter. Type some text. This is a rudimentary text editor, but it's good for quick notes or code. You can use the Enter key to go to the next line. Press Control + Z when you're finished editing the file. Press the Enter key. You'll see "1 file(s) copied," which means your file is now saved with the name you created. Another way to do this is to run this command: echo enter your text here > filename.txt.
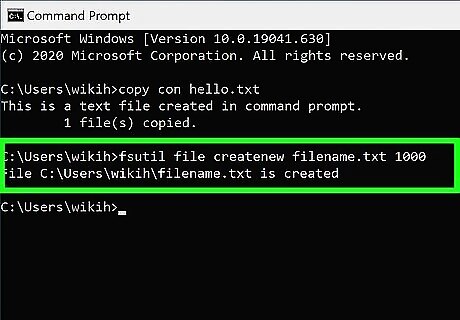
Create a file that's a certain size. If you don't want to create a file that's a specific size, skip this step. To create a blank text file based on byte size, use this command: fsutil file createnew filename.txt 1000. Replace filename with the desired file name, and 1000 with the actual number of bytes you'd like the file to be.
Deleting a File
Open the Command Prompt. The easiest way to do this is to press Win + S to activate the search bar, type cmd, and then click Command Prompt in the search results.
Go to the directory containing the file you want to delete. The prompt will open to C:\Users\YourName by default. If the file is somewhere else, type cd path_to_directory and press Enter. Replace path_to_directory with the actual directory location. For example, if you want to delete a file from the Desktop, type cd desktop and press Enter. If the directory you want to view isn't in your user directory (e.g., C:\Users\YourName), you'll have to type in the whole path (e.g., C:\Users\SomeoneElse\Desktop\Files).
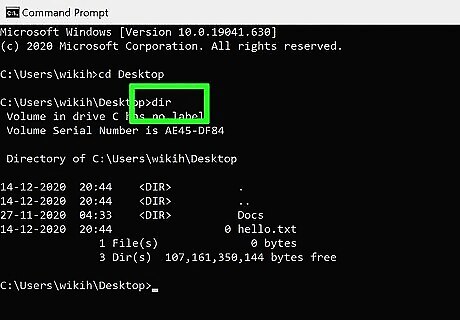
Type dir and press ↵ Enter. This displays a list of all files in the current directory. You should see the file you want to delete in this list. Using Command Prompt to delete files results in the files being deleted permanently rather than being moved to the Recycle Bin. Exercise caution when deleting files via Command Prompt.
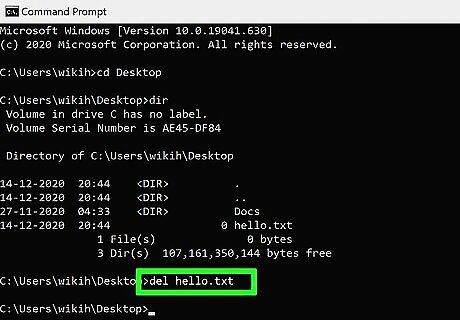
Type del filename and press ↵ Enter. Replace filename with the full name and extension of the file you want to delete. File names include file extensions (e.g., *.txt, *.jpg). This deletes the file from your computer. For example, to delete a text file entitled "hello", you would type del hello.txt into Command Prompt. If the file's name has a space in it (e.g., "hi there"), you will place the file's name in quotations (e.g., del "hi there"). If you get an error that says the file cannot be deleted, try using del /f filename instead, as this force-deletes read-only files.
Creating a Folder
Open the Command Prompt. The easiest way to do this is to press Win + S to activate the search bar, type cmd, and then click Command Prompt in the search results.
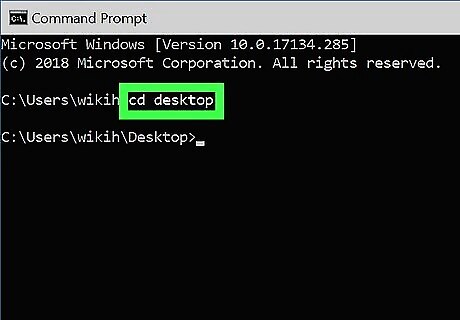
Go to the directory in which you want to create the new directory. The prompt will open to C:\Users\YourName by default. If you don't want to create a new directory here, type cd path_to_directory and press Enter. Replace path_to_directory with the actual directory location. For example, if you want to create a directory on your Desktop, you would type in cd desktop and press Enter. If the directory you're looking for isn't in your user directory (e.g., C:\Users\YourName), you'll have to type in the whole path (e.g., C:\Users\SomeoneElse\Desktop\Files).
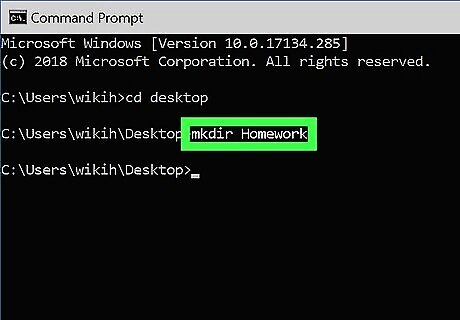
Type mkdir NameOfDirectory at the prompt. Replace NameOfDirectory with the name of the directory you wish to create. For example, to make a directory named "Homework", you would type mkdir Homework.
Press ↵ Enter. This runs the command to create a folder with the desired name.
Deleting a Folder
Open the Command Prompt. The easiest way to do this is to press Win + S to activate the search bar, type cmd, and then click Command Prompt in the search results.
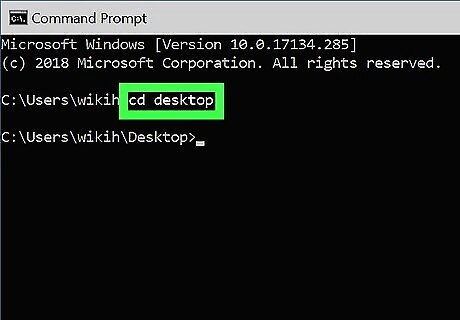
Go to the folder containing the directory you want to delete. The prompt will open to C:\Users\YourName by default. If the directory you want to delete is somewhere else, type cd path_to_directory and press Enter. Replace path_to_directory with the actual directory location. For example, if you want to delete a directory from your Desktop, type cd desktop. If the directory isn't in your user directory (e.g., C:\Users\YourName), you'll have to type in the whole path (e.g., C:\Users\SomeoneElse\Desktop\Files).
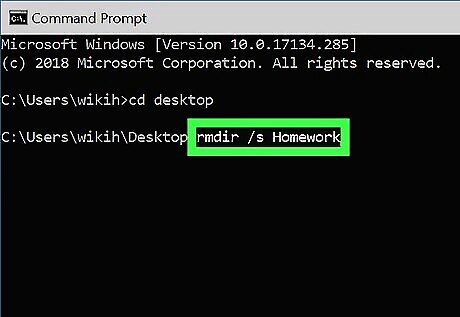
Type rmdir /s DirectoryName. Replace DirectoryName with the name of the directory you want to delete. For example, if you're trying to delete your "Homework" folder, you'd type in rmdir /s Homework here. If the directory's name has a space in it (e.g., "Homework assignments"), place the name in quotations (e.g., rmdir /s "Homework assignments").
Press ↵ Enter to run the command. If you try to delete a directory that contains hidden files or directories, you'll see an error that says "The directory is not empty." In this case, you'll have to remove the "hidden" and "system" attributes from the files inside the directory. To do this: Use cd to change into the directory you want to delete. Run dir /a to view a list of all files in the directory and their attributes. If you're still okay with deleting all of the files in the directory, run attrib -hs *. This removes special permissions from the undeletable files. Type cd .. and press Enter to go back one directory. Run the rmdir /s command again to delete the folder.
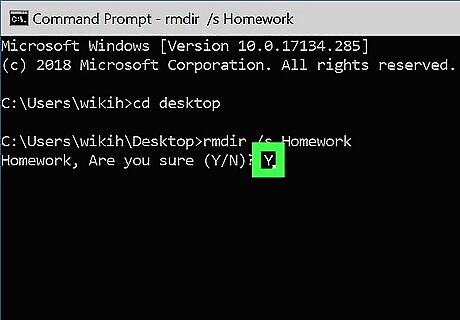
Press y and then ↵ Enter to confirm. This will permanently remove the directory.



















Comments
0 comment