views
X
Trustworthy Source
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Main public health institute for the US, run by the Dept. of Health and Human Services
Go to source
While there's no magic solution to immediately lower your blood pressure, there are a number of things you can do that can get you quick results. In this article, we'll go over a variety of natural solutions that you can start implementing today (like diet and lifestyle changes) to improve your blood pressure. So that you're fully informed, we'll also discuss the blood pressure medications currently available.
- Taking slow, deep breaths may help lower blood pressure immediately. You can incorporate breathing exercises into your daily routine for long-term benefits, too.
- Limit your sodium intake and eat plenty of potassium-rich foods like peas, spinach, bananas, kiwi, and watermelon.
- Aim to get in about 30 minutes of moderate exercise every day and 7-9 hours of healthy sleep every night.
Diet
Maintain a balanced diet. Dietary changes are usually the first step in dropping your blood pressure. A diet composed of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and dairy can lower your blood pressure by as much as 14 mmHg, especially when that diet also contains minimal amounts of saturated fats and cholesterol. If you focus on consuming foods known to drop blood pressure and accompany your diet changes with activity and lifestyle changes, your blood pressure will drop even faster.
Skip the salt. If possible, limit your sodium intake to 2300 mg a day or less. If you are older than 51 years of age or if you have underlying conditions causing an increased blood pressure, stick to 1500 mg of sodium a day at maximum. A small drop in your sodium intake can often lower your blood pressure by 2 to 8 mmHg. Check food labels on processed foods; they often contain a lot of sodium. To add flavor to your food, try herbs and spices like cayenne pepper (expands blood vessels and improves blood flow), turmeric (decreases inflammation, which improves cardiovascular function), garlic (lowers both cholesterol and blood pressure), and chili peppers.
Consume more potassium-rich foods. Generally speaking, try to get 3,000 to 3,500 mg of potassium every day. Good sources of potassium include milk, yogurt, peas, spinach, bananas, potatoes, tomatoes, orange juice, kidney beans, cantaloupe, honeydew, watermelon, kiwi, and raisins. Milk is packed with potassium and calcium, and both nutrients have been linked to low blood pressure. Dairy also contains vitamin D, which may also help. Studies indicate that drinking coconut water could help lower systolic blood pressure. In a study done by the American Heart Association, scientists discovered that eating three kiwis a day for up to 8 weeks could dramatically lower systolic blood pressure.

Limit or eliminate alcohol consumption. In small amounts, alcohol can actually cause your blood pressure to drop. However, the positive effects of alcohol can disappear after 2 drinks. In light to moderate amounts, wine and other alcohol can lower your blood pressure by 2 to 4 mmHg. In higher amounts, it may actually cause your blood pressure to increase. For men and women over the age of 65, drink one glass of wine or a beverage with a similar alcoholic content per day. For adults under the age of 65, you might be able to drink up to two glasses a day. For tracking purposes, one drink or glass equals 12 oz (355 ml) of beer, 5 oz (148 ml) of wine, or 1.5 oz (45 ml) of 80-proof liquor. Note that this is only helpful if you already drink alcohol, however. The results are less pronounced and riskier if you do not drink regularly. Drinking alcohol may decrease the effectiveness of blood pressure medication.
Drink hibiscus tea. Herbal teas containing hibiscus can lower blood pressure quickly and dramatically if you drink three cups on a daily basis. Steep the tea for six minutes before enjoying it cold or hot. Hibiscus tea contains anthocyanins and other antioxidants that strengthen your blood vessels, preventing them from narrowing and causing your blood pressure to spike. If you are taking a medication to lower cholesterol, such as simvastatin, talk to your doctor before you drink hibiscus tea.
Pour a glass of cranberry juice. A glass of low-calorie cranberry juice may lower blood pressure as effectively as a glass of red wine. Cranberry juice contains antioxidants known as proanthocyanidins. These nutrients restrict the body's production of ET-1, a compound known to constrict blood vessels and elevate blood pressure.

Incorporate tofu and soy products into your diet. Soy products contain isoflavones, nutrients that may have a direct link to lower blood pressure. Green tea and peanuts also contain a healthy amount of isoflavones.

Indulge in a bit of dark chocolate. Chocolate in general is rich in flavanols; these nutrients encourage the blood vessels to dilate wider, thereby lowering blood pressure. Since chocolate can be high in calories and sugar, eat it in moderation and fit it into your diet. For the most benefit, read the label to make sure that the chocolate you choose contains cacao and is low in sugar. Studies suggest that consuming chocolate can reduce blood pressure in individuals with high blood pressure, but the results are less pronounced in individuals with normal or near normal blood pressure.
Lifestyle
Take slow, deep breaths. Slow, meditative breathing relaxes the body, causing it to produce more nitric oxide and fewer stress hormones. To do a basic breathing exercise, take at least 5 minutes in the morning and 5 minutes to focus on inhaling deeply, taking deep "belly breaths" each time. Nitric oxide opens up the blood vessels, thereby reducing your blood pressure. Stress hormones elevate renin, a kidney enzyme linked to high blood pressure. For an even more pronounced effect on blood pressure, consider learning formal meditation, doing yoga, or trying Qigong or tai chi.
Listen to soothing music. Listening to soothing music for 30 minutes daily can help drop blood pressure, especially if done in conjunction with deep breathing techniques and hypertension medication. After as little as one week, your systolic reading can drop. Choose soothing music, like classical, Celtic, or Indian music.
Set aside 30 minutes a day for moderate-level exercise. Exercising for at least 30 minutes on most days of the week can quickly and substantially drop your blood pressure. You can get exercise through both athletic activities and common chores. Before increasing the amount of exercise you do in a day, ask your doctor for guidance. Increasing physical activity too dramatically may put you at greater risk of heart attack or stroke. Power walking is one of the simplest exercises you can add to your routine. Walking at a brisk pace for 30 minutes can lower your blood pressure by nearly 8 mmHg. Other athletic activities you can try include volleyball, touch football, shooting baskets, bicycling, dancing, water aerobics, swimming, and jumping rope.

Reduce the number of hours you spend working. Working over 40 hours per week increases your risk of developing high blood pressure. If you need to quickly lower your blood pressure, you should try shaving off a little time from your work schedule when possible. This is especially significant if your job is notably hectic or stressful. Stress hormones cause your blood vessels to constrict, which only makes it harder for your heart to pump blood through them. As a result, your blood pressure rises.
Get 7-9 hours of restful sleep every night. To create a sleep schedule, work on going to bed and waking up at the same time each day and make sure your sleeping space is cool, quiet, and dark to help you stay asleep. If you have a hard time winding down at the end of the day, try taking a warm bath or doing simple stretches about an hour before bed. It also helps to avoid bright light from screens at least 30 minutes before going to sleep. Regularly getting less than 6 hours of sleep a night can contribute to hypertension.
Quit smoking. Nicotine is one culprit behind high blood pressure. If you smoke or are around people who smoke, cutting this from your life is one way to quickly drop your blood pressure. Smoking increases your blood pressure up to an hour after you smoke. If you smoke continually, your blood pressure will be continually elevated. The same effect applies to people who are continually around smokers.
Supplements and Medications
CoQ10 supplement - Coenzyme Q10 is a natural supplement and antioxidant that has the ability to reduce blood pressure by 17 mmHg (systolic) over 10 mmHg (diastolic) when taken regularly. The supplement dilates your blood vessels, making it easier for the heart to pump blood through them. Ask your doctor about the supplement. They may recommend that you take a 60 to 100 mg CoQ10 supplement up to three times daily.
Diuretics - Diuretics flush excess sodium and water out of the body. Since sodium is a known culprit of high blood pressure, the removal of excess sodium can cause a significant drop in blood pressure.
Beta-blockers - Beta-blockers cause the heart rate to drop. As a result, the heart pumps out less blood, thereby lowering your blood pressure.
ACE inhibitors - ACE stands for "Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme." This enzyme causes your body to produce angiotensin, a chemical responsible for constricting the arteries throughout the body. An ACE inhibitor causes your blood vessels to open, making it easier for blood to flow through them and causing your blood pressure to drop.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers - This medication directly blocks the effect of angiotensin, which is responsible for causing the arteries to constrict. Angiotensin needs to join with a receptor in order to affect the blood vessel. These medications block the receptors, thereby preventing the chemical from having an impact.
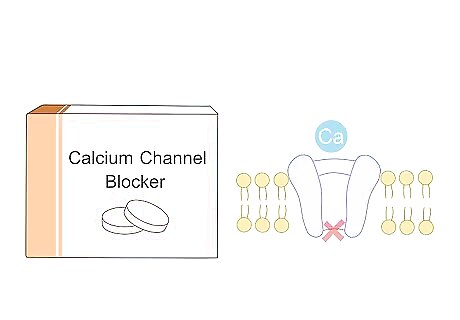
Calcium channel blockers - Calcium channel blockers work by blocking calcium from entering the heart and arteries. Calcium causes smooth muscle cells in these areas to become hard, which means that the heart must use more force to pump blood through the arteries.This medication relaxes narrow blood vessels, thereby lowering blood pressure.
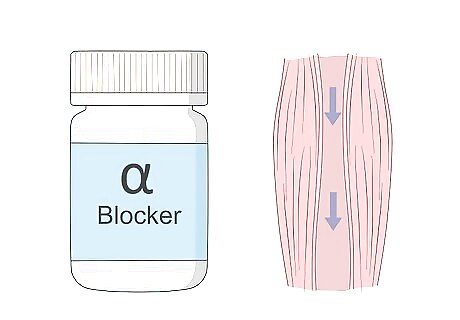
Alpha-blockers - Alpha-blockers reduce resistance in the arteries. As a result, vascular muscles relax, making it easier for blood to flow through.
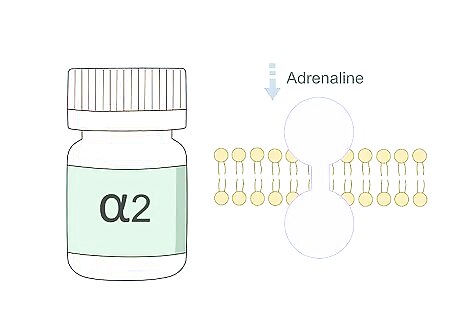
Alpha-2 receptor agonists - This medication reduces the function of the sympathetic part of the involuntary nervous system. This means that less adrenaline is produced. Adrenaline, along with other stress hormones, can cause blood vessels to constrict.
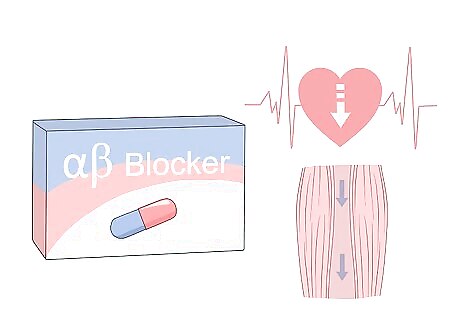
Combined alpha-beta-blocker - These are the first line of defense for patients facing crucially high blood pressure and drop blood pressure quicker than most other medications. This medication reduces the resistance put up by your arteries and causes your heart rate to drop.
Central agonists - These medications prevent your blood vessels from contracting quite as easily, thereby making it easier for your blood to flow through them. Note that the effect is similar to that accomplished by alpha-beta-blockers.
Peripheral adrenergic inhibitors - The brain is the primary target of this group of medications. Neurotransmitters responsible for telling the smooth muscles of your heart and blood vessels are blocked when taking these medications, so the message telling those blood vessels to constrict never reaches its destination.
Blood vessel dilator or vasodilator - These medications only cause the blood vessel muscles to relax. As a result, they dilate, allowing blood to flow through with less pressure.















Comments
0 comment