
views
X
Expert Source
Siddharth Tambar, MDBoard Certified Rheumatologist
Expert Interview. 25 August 2020.
You may feel a lot of pain and discomfort in one or more of these joints for a short period of time and often at night.[2]
X
Research source
Gout is caused by an excess of uric acid (hyperuricemia) in the blood. Sometimes, uric acid crystallizes and accumulates in the joints, causing pain and tenderness. By closely observing the level of comfort and mobility in your joints, as well as identifying patterns in your pain and identifying any risk factors, you should be able to better recognize gout symptoms and seek effective medical treatment.
Recognizing Symptoms in the Joints

Touch your big toe. Ask yourself whether it feels very sensitive and painful. Pain and discomfort in the big toe is a common sign of gout.
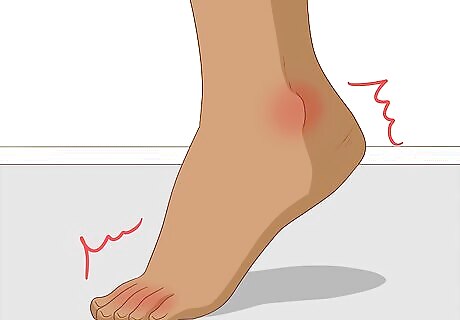
Review the comfort of your toes, ankles, knees, fingers, wrists, and elbows. Consider whether any of these joints feel uncomfortable or painful. Gout can impact any joint in the body but most commonly manifests in these joints. If you are experiencing discomfort in one or more of these joints, your doctor may come to the conclusion that you have gout.
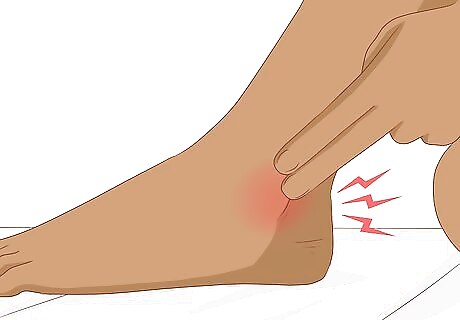
Consider whether your joint feels hot and tender. Touch your joint and feel whether it is hot and tender. If so, you may be experiencing a symptom that is common with gout.
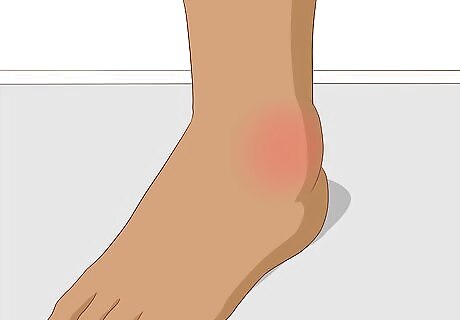
Check for swelling in and around the joint. If you see redness and swelling of the joint, you are experiencing another symptom that is commonly associated with gout.

Look for red and shiny skin where you are experiencing pain. If the skin around the joint is very red and shiny, you have another symptom of gout. Consider whether your skin looks very red around your joints, which is also common with gout.
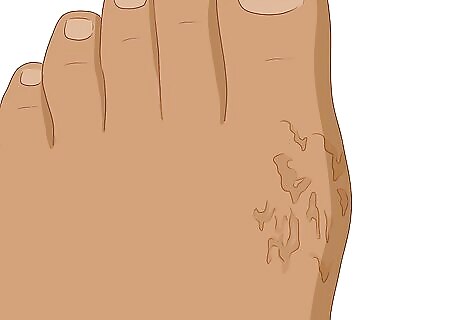
Look for peeling or flaky skin around the joint. This symptom is also commonly associated with gout. Check if the skin is flaking off your ankles or toes. If you have a lot of flaky skin, this could be a sign of gout.
Ask yourself whether you have limited mobility in the impacted joint. This is another common symptom of gout. For instance, try wiggling your big toe up and down. If you are able to do this movement without pain, it is a good sign. If you are able to move it all the way up and all the way down, it is also a good sign; however, if you are unable to move it freely and without pain, you may be experiencing gout.
Recognizing the Pattern of Symptoms
Determine if your pain is mostly at night. Although the pain of a gout attack can come at any time of the day, most people experience it the worst at night.
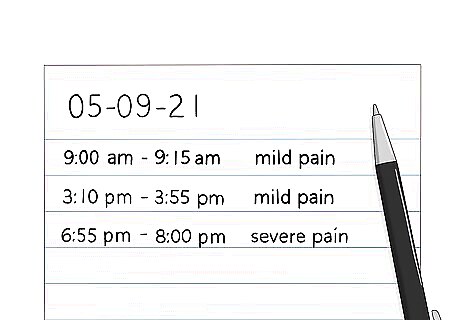
Record the intensity of your symptoms. Determine whether your joints feel very painful all of a sudden and for a few hours at a time. Gout attacks typically develop fast and over a few hours at the beginning stages of the condition. An acute gout attack will be most painful about 12 to 24 hours after it starts.
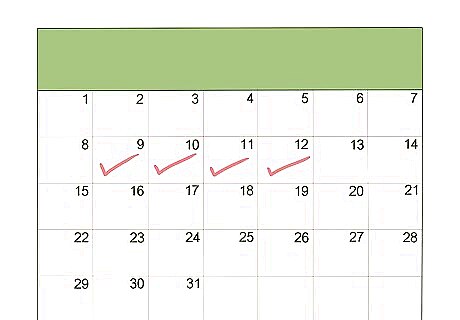
Record the total duration of your painful attacks. Typically, a gout attack will last between three and 10 days. If the attack is not treated, it will last longer. Try recording the duration of your symptoms in a health journal.
Figure out whether your symptoms are becoming worse over time. If untreated, gout symptoms (e.g., pain, swelling) will become worse over time. If you are experiencing these symptoms, you should see a doctor.
Recognizing Whether You Are at Risk for Gout

Figure out whether you are in a high risk demographic. Typically, men are at a higher risk for gout than women and the level of risk increases with age. So, older men are definitely at an increased risk for gout. The risk for gout increases significantly for women who have already gone through menopause. Men are at highest risk of developing gout between the ages of 30 and 50.
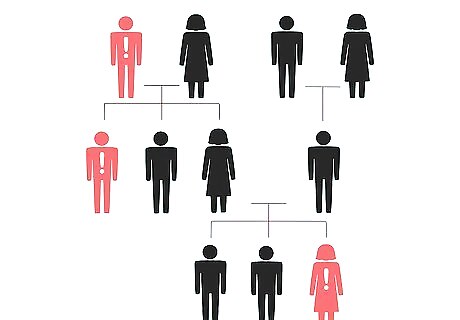
Look into whether you have a family history of gout. Figure out whether your father, mother, grandparents, or great grandparents experienced gout. You could ask your parents or other family members if they know of any family history of gout. If you have a family history of gout, you are more at risk of getting it.
Find out if you are overweight. If you are too heavy, your body makes more uric acid and your kidneys have a harder time getting rid of it. These factors make you more susceptible to gout. Use a body mass index calculator online. This index is a measure of body fat based on height and weight. Enter your height and weight into an online body mass index calculator, and then hit “calculate.” You can then compare your body mass index to the healthy index projected for your age and sex. Ask your doctor to determine whether you are overweight. Your doctor has a number of different measurements and tools that they can use to determine your current and healthy weight.

Assess your diet with a food diary. Write down everything you eat for one week in order to determine your level of consumption of meat, seafood, sugar, and alcohol. Once you have tracked your level of consumption of these items for one week, you should review your patterns of consumption (e.g., how often you drink sugary soft drinks and at what times of the day). If you regularly consume a lot of meat, sugar, and alcohol, you are at a higher risk for gout. Findings suggest that if men maintain a diet that has a lot of sugar from soft drinks they are more likely to get gout. Drinking soft drinks on a daily basis will greatly increase your risk. Eating a diet with a lot of meat and seafood (high-purine foods) is a risk factor for gout. Alcohol consumption is a trigger for gout attacks. Drinking will likely trigger an attack within 24 hours and your risk increases relative to the amount you drink. If you are unsure of your diet, you could go see a dietitian or doctor. It can help to bring your food diary with you, so they have an idea of how much sugar, meat, and alcohol you currently consume.
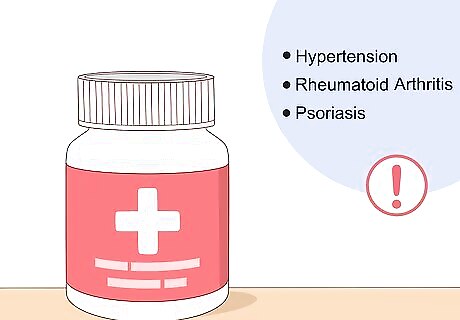
Assess medications that may increase risk. Medications used to treat hypertension as well as drugs that suppress the immune system, such as those prescribed to people to treat rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, or who have undergone an organ transplant can sometimes increase the risk of gout.

Reflect on your recent history of surgery and trauma. If you have recently experienced surgery or trauma, you may also be at a higher risk for gout. If you have any kind of surgery, you are at an increased risk. Undergoing chemotherapy can also be a trigger for gout.




















Comments
0 comment