
views
X
Research source
Whatever your reason for wanting one in your yard, you have two options: sowing seedlings or transplanting a young tree.
Planting Mesquite Seeds

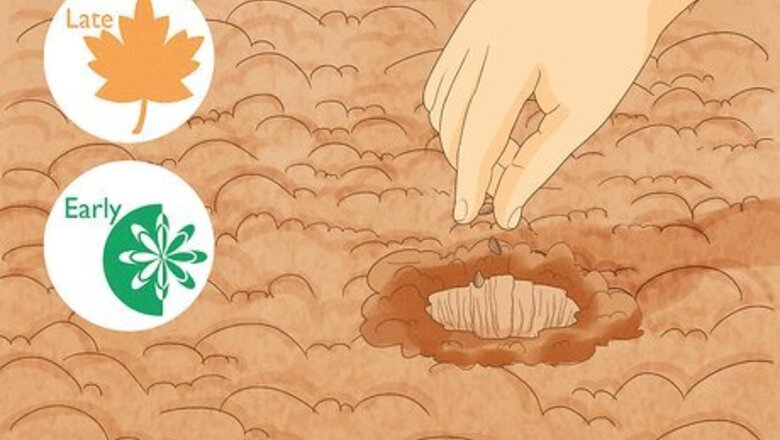
Plant your mesquite seeds during early spring and late fall. Since weather can vary by region, always plant during times when soil temperature is around 80 °F (27 °C). Seedling growth slows when temperatures exceed 95 °F (35 °C).
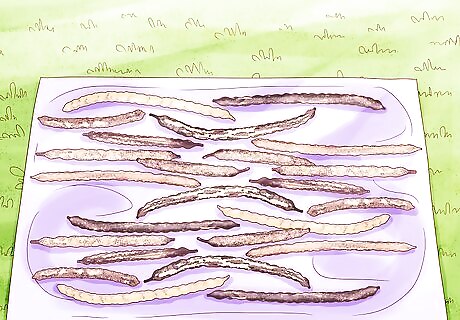
Dry your pods out for 1 to 3 days to prevent fungal growth. Lay your pods in the sun on a cloth, metal roofing, or the hood of your car. Properly dried pods should snap in two when you bend them. If they don't, they're not dry enough. Wetting or washing pods increases the chances of fungal growth.
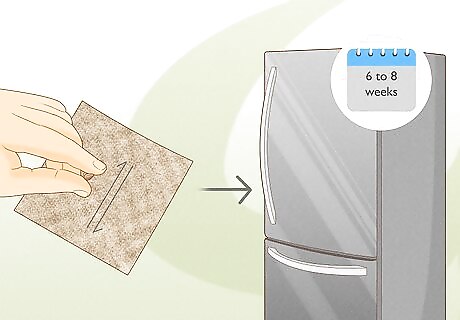
Scarify your seeds prior to planting. Scarification is the process of removing the coat off of your seeds, which allows moisture and oxygen into their embryos. This process mimics the natural process a seed would experience traveling through an animal's gut before being expelled. Use sandpaper or a small file to knick the seed coat. Afterward, put your seeds in the refrigerator for 6 to 8 weeks before planting to mimic the process of stratification.
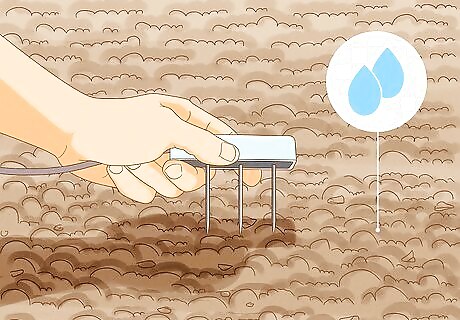
Choose a planting location with plenty of soil moisture. For at least 3 to 5 days after sowing your seeds, the soil must be moist. Use a soil moisture sensor to determine its suitability. Light is not necessary for germination, so shady spots are fine. Add organic matter to improve soil moisture retention. During growing season (typically April until October or November), high to medium-fertility soils like worm compost or garden compost are best. Low-fertility soil improvers such as leaf mould can be added during any season.
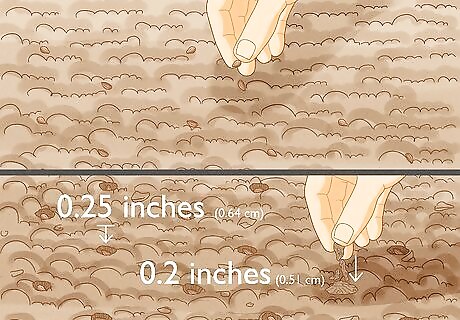
Sprinkle your seeds evenly over the ground before covering them with soil. After layering them on the soil, use your hands to dig them approximately 0.25 inches (0.64 cm) below the soil and cover them with an additional 0.2 inches (0.51 cm). The soil must be at least 77 °F (25 °C) for the establishment of seedlings. They grow fastest when soil temperatures are between 80 to 90 °F (27 to 32 °C). Seedling growth begins to decline when soil temperatures exceed 95 °F (35 °C).
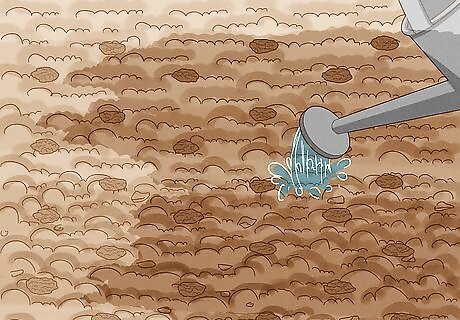
Water the seeds regularly after you plant them to keep the soil moist. After sowing your seeds into the soil, keep it consistently moist. Seedlings usually establish 10 days after this period. Sprinkle mulch over the top of the soil if you want to cool roots and promote moisture retention.

Continue to tend to the seedlings after they sprout. Seedling establishment is signified by the full development of the first leaf, which marks the beginning of the juvenile stage. During this phase, optimal soil temperature is 85 to 90 °F (29 to 32 °C). Continue watering your seedlings regularly to maintain soil moisture. With proper soil temperature and moisture, plants in the juvenile stage will grow up to to 5 to 6 feet (1.5 to 1.8 m) tall in 2 to 3 years. Keep an eye out for insects and animals. If the plant tops are removed below the cotyledon (an embryonic leaf), the seedling can be destroyed.
Water your mesquite tree once or twice each week. After your tree develops woody xylem tissue, it has left the juvenile stage and entered the mature stage. During this period, water your tree once or twice a week, using enough water to soak the top 2 to 3 feet (0.61 to 0.91 m) of the soil. Compared to shallow watering, deep watering gives the roots of your tree enough time to absorb the water.
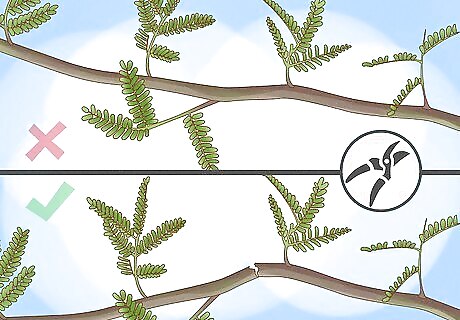
Prune your tree after 2 years of growth in the mature stage. Avoid pruning before this time, as many small branches during the growth period are needed for trunk protection and strength. Focus on overcrowded, crossing, and broken branches. Cut at the base of your tree's branches to promote faster healing, leaving the branch collar intact. Don't prune more than 20 to 30 percent of your tree in one session. Prune during spring and late winter to promote growth; prune in the summer to reduce tree size; skip pruning during the fall.
Transplanting a Young Mesquite Tree

Plant your mesquite tree during early spring or late fall. Soil moisture is most favorable for growth during these periods. Plant your trees within 15 feet (4.6 m) of your home to offer shade in the warmer months. If your soil isn't holding moisture, add organic matter to improve water retention.
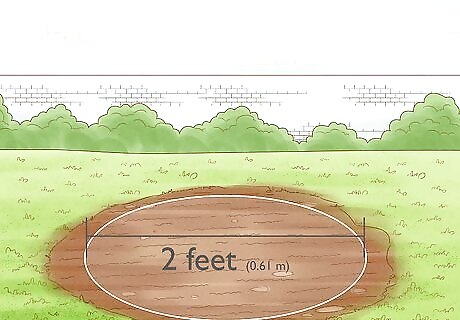
Choose a planting location with a diameter of 2 feet (0.61 m) or more. Mesquite trees can grow to about 25 feet (7.6 m) in height, with support stems hitting as much as 2 feet (0.61 m) in diameter. Make sure you choose a location that will give them room for growth. A seedling 3 inches (7.6 cm) tall will have a taproot 8 to 10 inches (20 to 25 cm) long.
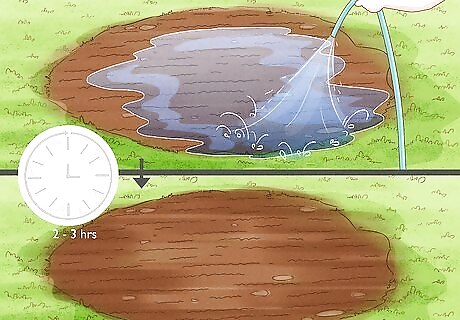
Test the soil to make sure it’s well-draining. Pour water around your planting area. Check back in 2 to 3 hours and see if the water has drained. If it has, your area is properly drained. If not, consider another location, amend your soil with sand, or create a berm. Also known as an "eyebrow," a berm is a small hill beyond the drip line that holds water where the tree requires it most. Make sure that the highest point of the berm is on the side of the tree that slopes down. Leave an opening in the upslope side of the berm to help it catch water running down from higher elevations.
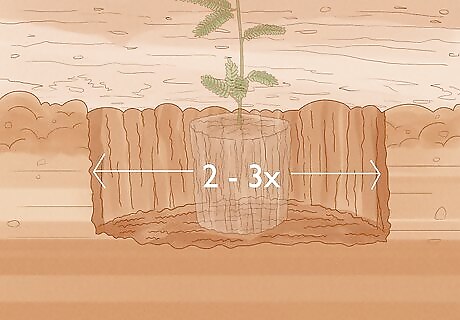
Dig a planting hole in your desired location. The hole should be no deeper than the root ball and approximately 2 to 3 times as wide. Use a shovel to slope the edges of your hole so that roots have an easier time penetrating the soil. Plant your tree level in the soil. A planting hole deeper than your root ball can prevent gas and nutrient exchange at the base of the trunk. It can also cause the tree to fall.

Use a shovel to transfer the tree from its planting container into the hole. If the tree has become root-bound, use your hands to loosen it. You can also use a pocket knife to cut along the side of the ball and allow the roots to grow outwards. Fill the hole back up with the soil you removed.

Avoid using special amendments. Optimal soil for your transplanted tree is the soil that it is adapted to grow in. If your mesquite is native to your area, it will grow just fine without amendments like alfalfa meal, bone meal, and compost. The soil removed to make the hole should always be used to refill it.
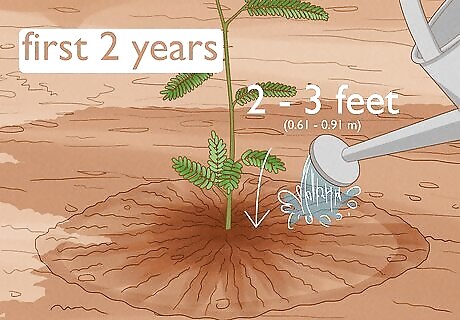
Water your mesquite tree once or twice a week. Use enough water to soak the top 2 to 3 feet (0.61 to 0.91 m) of your soil 1 to 2 times a week. Compared to shallow watering, deep watering gives the roots of your tree enough time to absorb the water. Newly transplanted trees need to be watered regularly for the first 2 years. After 2 years, it will continue to grow without additional watering. However, a bit of extra water in the hot summer months is recommended. Always water your trees along their drip lines, which is the outermost circumference of the canopy where water drips onto the ground. Never water at the base of the trunk. Create a drip irrigation system to optimize water efficiency.

Prune your tree after the first 2 years. Even if your tree starts to look wild, avoid pruning until 2 years have passed. The small branches from its early years are important for trunk protection and strength during the growth period.




















Comments
0 comment