views
Distinguishing Warts from Other Skin Issues
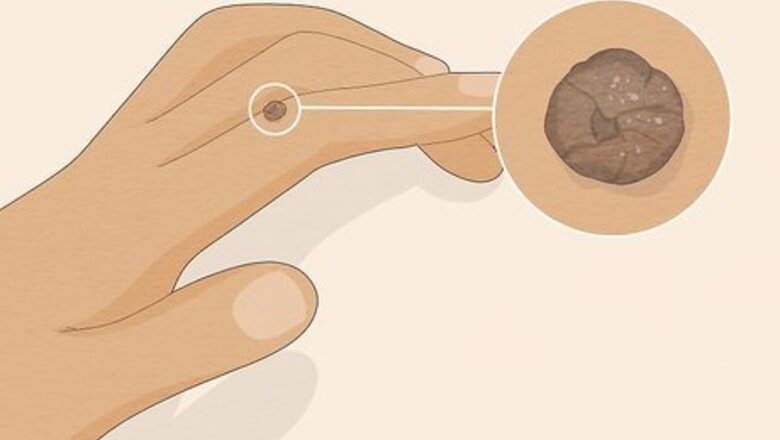
Look for small, gray or flesh-colored bumps of skin. Warts are fleshy bumps of skin that may be light gray or the same color as your skin. They're usually small, and range in size from 1 to 10 mm (0.039 to 0.394 in). You might notice a single wart, or see them growing in clusters. Warts don't have heads like pimples, but there might be a small black dot in the bump that looks like a tiny seed. Sometimes, the blood that feeds a wart dries inside and forms a small black spot. These spots are called thrombosed capillaries. Warts are caused by viruses; different viruses cause different kinds of warts and affect various parts of the body.
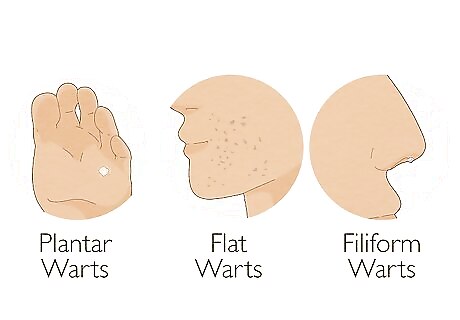
Determine what type of wart you have. You can get a common wart on any part of your body, especially your hands. They often appear as a raised, flesh-color bump with an irregular surface. These warts are most typical, but there are other types of wart. Here's how to identify them: Plantar warts develop on your feet, especially on the weight bearing parts. They are usually hard and may have a black dot in the center, which is a broken blood vessel. Flat warts usually occur on your face, hands, and feet. They often look like a grouping of flat-top, flesh-colored bumps. They can also be dome-shaped. Filiform warts, which most often appear on your face, lips, nose, and eyelids, look like thin stalks, similar to a skin tag. Sometimes you might have a cluster of stalks in a circle.
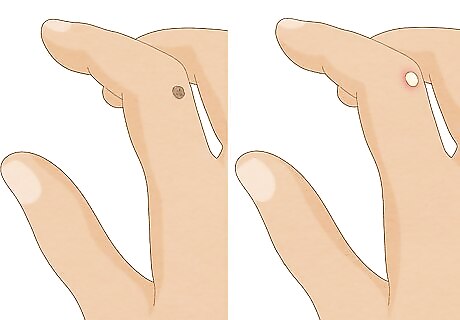
Distinguish between hard warts and liquid-filled blisters. If your bump feels hard and fleshy, it might be a wart. Soft bumps that feel like they have liquid inside are a different type of skin growth, like a cyst. Wash your hands with soap and warm water for at least 20 seconds after touching a wart or the skin around it. It's easy to spread the viruses that cause warts.
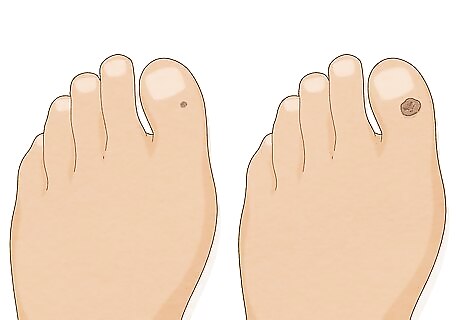
Pay attention to how quickly the bumps developed. Usually, warts take around 2 to 6 months to grow to a noticeable size. Even the fastest-growing warts develop over the course of days or weeks, so bumps that appear suddenly are most likely due to another issue. If your bumps suddenly appeared over a matter of minutes or hours, they might be due to an allergic reaction. Hives, or small pink bumps associated with an allergic rash, are also itchy. Warts usually aren't itchy or painful. Plantar warts, which grow on the soles of the feet, sometimes get pressed by the force of walking, which can be painful.
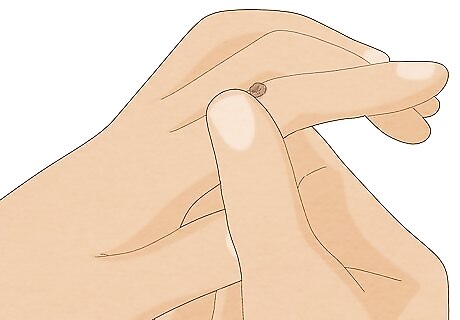
Check for rough, smooth, or stringy surfaces. The texture of the surface can help you and your doctor determine the best course of treatment. Common warts are usually rough or grainy, a bit like the texture of cauliflower. Some warts are smooth, flat and skinny, while others look like clusters of little threads or strings. Common warts, which usually have rough surfaces, are often easily treated with over-the-counter medication. Other warts might require alternative treatment methods, such as medication that boosts the immune system.
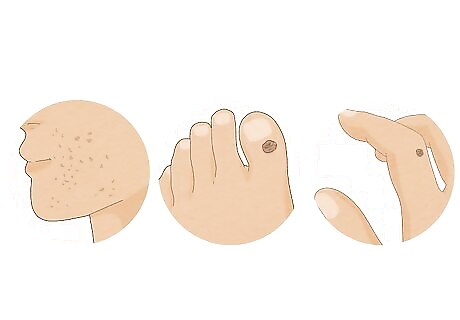
Note where warts are appearing on your body. Warts can appear just about anywhere on the body, and the right treatment depends on the location. They often grow on sites that have experienced an injury or that bear a lot of weight. Common locations include the fingers, hands, elbows, knees, and feet. For these spots, over-the-counter salicylic acid should do the trick. For warts that affect sensitive skin, such as your face, it's best to have your doctor or pharmacist recommend a treatment method. Salicylic acid, for instance, shouldn't be used on the face. You should always see a doctor if you suspect you've contracted genital warts. If you don't have a primary doctor, you can seek treatment at a local sexual health clinic.

See your doctor for an accurate diagnosis. While warts are often treatable at home, you should see a doctor if warts are widespread, hurt, or if they don't respond to home treatment. A widespread outbreak of warts could indicate an immune system issue. Additionally, you should always see a doctor if you believe you have genital warts. Dark or multi-colored, irregularly shaped warts can sometimes resemble some forms of skin cancer, so your doctor might want to take a biopsy, or a small tissue sample, just to stay on the safe side.
Treating Warts
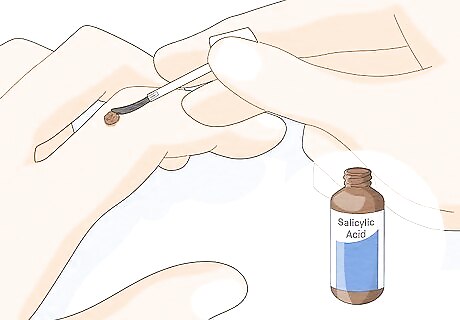
Treat common warts with an over-the-counter topical medication. For common warts on your fingers, hands, arms, or legs, apply a wart removal medication that contains salicylic acid or lactic acid. Read your product's instructions, and use it as directed. It can take multiple weeks for these treatments to yield results. If the label advises, soak the area for 10 minutes in warm water and buff the wart with an emery board before applying the medicine. This can make the medicine more effective. Throw out the emery board after buffing the wart, and don't use it file your nails or share it with anyone. Topical medications come in gel, plaster, or bandage forms. You should only apply the medication directly to the wart. Do not use it on any other parts of your body. Side effects may include burning or redness at the application site. Remember that salicylic acid shouldn't be used on the face. If warts affect sensitive areas of skin, ask your doctor or pharmacist to recommend the best treatment option. Use your over-the-counter salicylic acid medication every night before bed for up to 12 weeks. Be sure to follow your doctor’s recommendations.
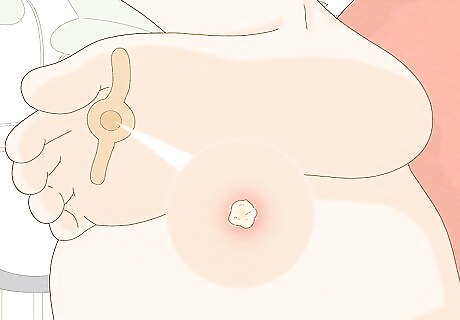
Treat plantar warts with a 40% salicyclic acid plaster. First, use a pumice stone to buff the wart, removing dead skin cells around it. Then, cut the plaster to fit the size of your wart. Apply the plaster to the wart and leave it on for 24-48 hours. Buff the wart with the pumice stone again, then reapply the plaster until your wart goes away (or until you see the doctor again). Don't use the pumice stone on any other area after you've used it on the wart. After the treatment is complete, discard the pumice stone. You should get relief from pain after the first 24-48 hours. The pumice stone and the salicylic acid will both irritate the skin on the wart. This can help your body develop an immunity to that strain of wart, and when that happens, it should go away.
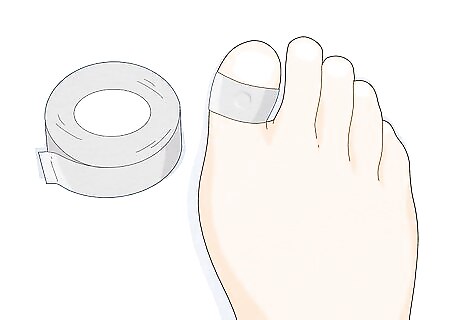
Try covering a wart with duct tape for 5 days. Cut a square of duct tape to fit the area, then place it over the wart. Change the tape if it no longer sticks to your skin. After 5 days, leave it uncovered for 1 night. If buying medication or seeing a doctor aren't options, duct tape could be an effective home remedy. Though some doctors do recommend taping, keep in mind there's mixed evidence of its effectiveness. It's best to only use this method on areas that aren't highly visible. Don't use it on your face!
Get a prescription if an over-the-counter medication doesn't work. Consult your doctor if you've tried over-the-counter medications for 2 to 3 months without success. They might apply a prescription-strength topical medication at their office, or have you apply medicine at home. Since prescription-strength medications have a stronger concentration of acid, it's important to follow your doctor's instructions carefully. Improper use could harm your skin. Additionally, you might need a prescription for medication that's safe to use on your face or other sensitive areas of skin.
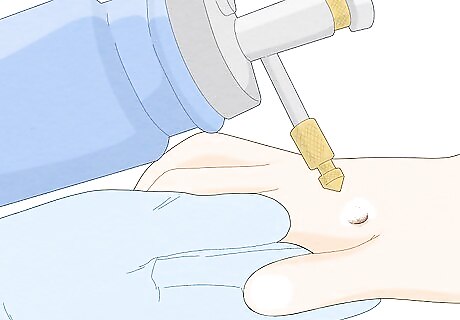
Ask your doctor or pharmacist about cryotherapy. Cryotherapy, or freezing the warts with liquid nitrogen, is one of the most common treatment methods, especially for warts that affect the face. Side effects include minor pain and dark spots at the application site. Depending on the severity of the outbreak, treatment could involve multiple cryotherapy sessions over 3 to 4 months. You can also find over-the-counter liquid nitrogen wart removal kits at your pharmacy. Check your product's instruction label, and use it as directed. Apply liquid nitrogen only to the wart, and don't use it on any other parts of your body.
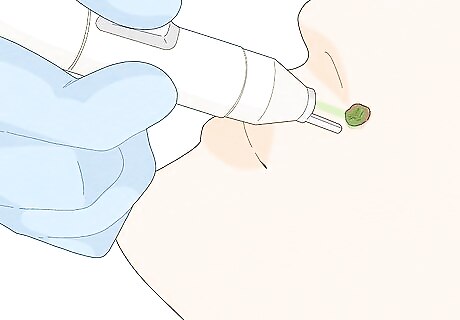
Manage a widespread outbreak with electrosurgery or laser therapy. For widespread, persistent, or severe outbreaks, your doctor might recommend electrosurgery or laser therapy, which involve burning and cutting away the warts. You might need multiple treatment sessions over the course of a few months. Side effects of electrosurgery may include pain, burning, or discomfort. Laser therapy might cause some discomfort, but it's usually painless. For both methods, scarring is possible. Don't try to cut or burn a wart by yourself.
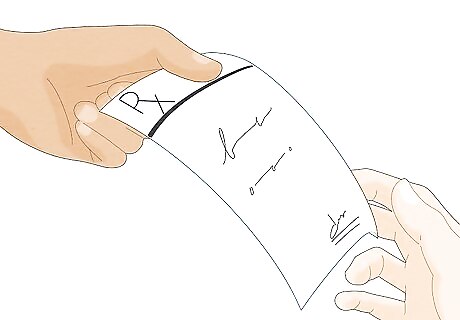
Discuss treatment options with your doctor if you have genital warts. Never attempt to treat genital warts on your own or apply over-the-counter medications to the area around your genitals. These medications are not effective against genital warts. Skin in these areas is also sensitive, and over-the-counter treatments could cause damage. Depending on the location and severity of the outbreak, your doctor will prescribe a topical cream or gel, perform cryotherapy, or recommend laser therapy. Apply any medication according to your doctor's instructions. Don't stop using a medication without consulting your doctor.
Preventing Warts from Spreading
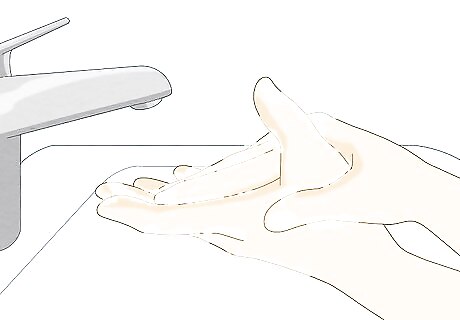
Wash your hands often, especially if you have a cut. Healthy hand hygiene is always a must, whether or not you have warts. It's even more important to wash your hands often if you have a cut or broken skin, which makes you more susceptible to the viruses that cause warts. If you're treating warts, wash your hands with soap and warm water for at least 20 seconds after applying wart removal medication. Always wash your hands after you go to the bathroom, before you eat, after touching your face, handle raw meat, touch any soiled surfaces, or come into contact with someone who has warts.
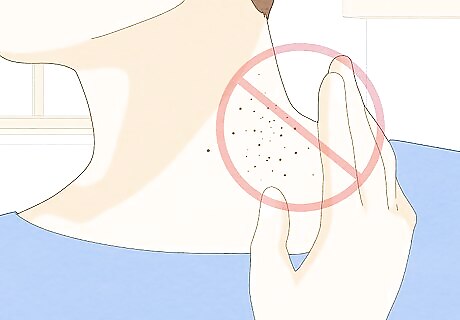
Avoid touching, scratching, or biting the affected areas. While treating warts, it's essential that you leave them alone. Medications used to treat warts don't actually kill the viruses that cause them. It's possible to spread warts elsewhere on your body or to other people, even while undergoing treatment. Scratching or biting can also worsen existing warts or cause an infection.
Don't share towels, footwear, or clothing with other people. Remind anyone you live with that they shouldn't borrow your towels, clothes, socks, shoes, or personal hygiene products. If someone else has warts, don't share any towels, articles of clothing, or personal hygiene products with them. Even if you don't have warts, it's wise not to share used towels, garments, or hygiene products.

Clean the bottom of your shower or bath if you have plantar warts. Warts that affect the soles of feet are called plantar warts. After you shower, wash the bathtub with an disinfectant cleaner or a solution of 1 part bleach to 10 parts water. Spray the cleaning solution onto the tub, scrub the area with a paper towel, then rinse it thoroughly with hot water. Wash your hands when you're finished.
Practice safe sex and avoid sex during an outbreak of genital warts. Don't engage in any form of sexual contact while genital warts are present. Inform your sexual partners that you've received treatment for genital warts, and always use a condom during sex. Since genital warts can affect areas that aren't covered by a condom, it's still possible to spread the virus even if you practice safe sex. It's easier to spread genital warts during an outbreak. However, spreading the virus that causes them is still possible when no warts are present.



















Comments
0 comment