views
Changing Output Text Color
Include the Standard Input and Output library. This common library allows you to change the color that the text output displays. Add the following code to the top of your program:
#include
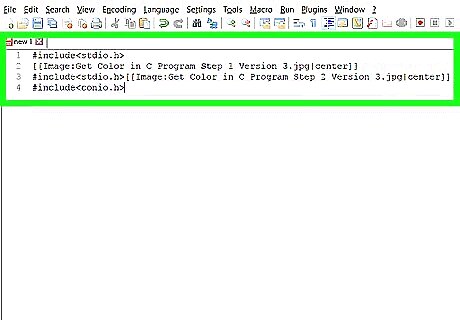
Include the Console Input and Output library. This will make it easier to capture keyboard input from the user. Add the library below the stdio.h library:
#include
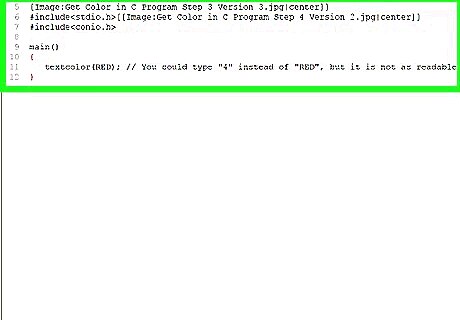
Use the textcolor function to define what color you want to use for text. You can use this function to vary the text colors of your output. Colors must be written in all caps, or expressed as a numeral:
#include
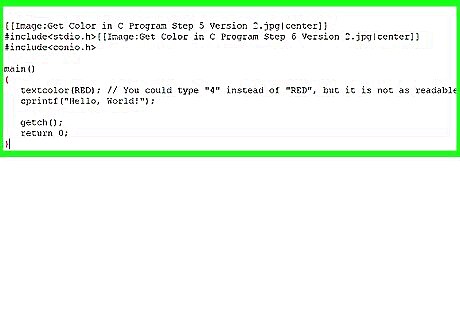
Add output text and finish the program. Include a cprintf function to display some text in your new color. Use a getch function at the end to close the program when the user presses a key.
#include
Changing Drawing Color
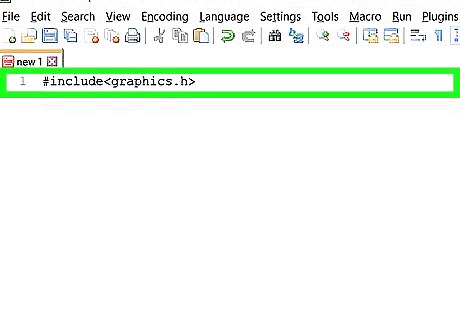
Include the graphics library. The C graphics library allows you to draw objects, as well as adjust their color. You can get access to the graphics library by including it at the top of your program:
#include
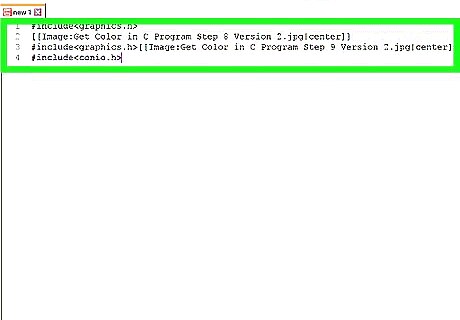
Include the Console Input and Output library. You can use this library to easily capture a user's input. Add the library below the graphics.h library:
#include
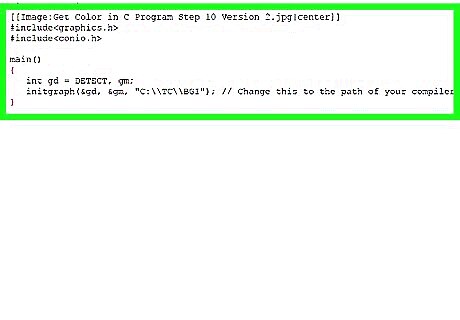
Initialize the variables for the graphics driver and mode. You'll need to do this before you begin drawing objects, so that the program has access to the system graphics drivers. This will create an area on the screen that the object will be drawn on.
#include
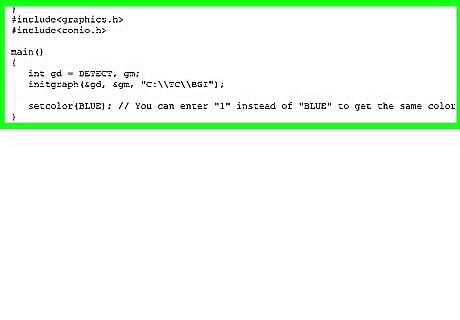
Set the color of the object you want to draw. Before coding in an object, use the setcolor function to define the color of the object you are about to draw:
#include
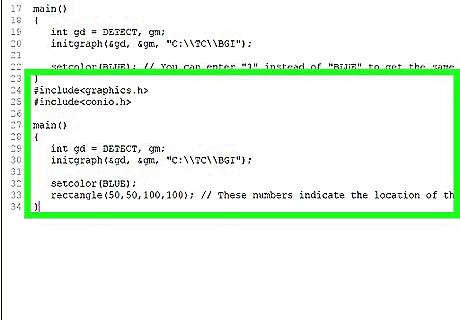
Draw an object of your choice. For this example, you'll be drawing a rectangle using the rectangle function. You can use any of the graphics.h drawing tools to draw in the color that you set.
#include
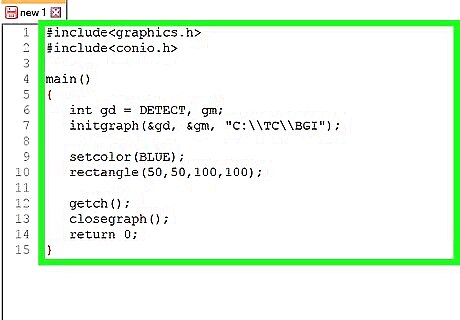
Finish off the program and test it. Add the getch command and turn off the graphics area as you close the program. Compile it and give it a test run.
#include


















Comments
0 comment