
views
- Apply a generous amount of sunscreen whenever you spend time outside, especially on your face and ears.
- Wear long-sleeve shirts, hats, and other clothing that covers your skin.
- Use makeup or lotions with built-in sun protection for long-term, passive skin care.
Protecting Your Skin

Wear sunscreens and sun blocks. Lotions, creams, and blocks that protect from the sun work in different ways, but they are all designed to protect your skin from damage, and this will prevent your skin from getting dark in the sun. Sunscreen filters the UV radiation that passes through to your skin. Look for a broad-spectrum sunscreen, which protects from UVA and UVB, with an SPF of at least 30. Sunscreen gels are good for hairy parts of your body, like your scalp. Sunblock creates a physical barrier between the sun and your skin. Look for broad-spectrum, an SPF of at least 30, and ingredients like octyl salicylate and methoxycinnamate, and octocrylene. Apply sun-protective lotions about 30 minutes before going outdoors, and use at least an ounce of sunscreen at each application. Reapply after swimming, activities that caused you to sweat, or every two hours. Most sunscreens will block your pores, so get one specifically made for facial application if you have oily or acne-prone skin.
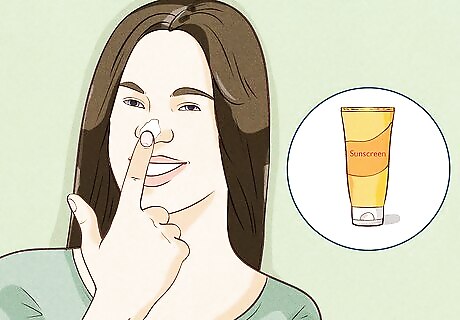
Apply sunscreen to commonly missed body parts. Sunscreen or sunblock is only effective on the areas of the body you apply it to, and there are some areas that people often forget. Don’t forget to apply sunscreen to your: Nose Tips of your ears Scalp Lips Eyelids

Wear makeup with an SPF. Most moisturizers, bronzers, foundations, and lipsticks these days are available with built-in sun-protection. For an extra layer of protection for your face, choose cosmetics that have an SPF rating of at least 15. Because you only apply makeup once in the morning, you can't rely on it for all your sun protection. Use SPF makeup in conjunction with your other sun precautions. You should still apply a base layer of sunscreen to your face before applying makeup.

Wear sunscreen every day. This still applies even if you don’t plan to go outside. Your skin is still exposed to UV rays inside, because UV passes directly through glass and windows in buildings and houses. Wearing sunscreen to be in the car is also important, because UV also passes through car windows.

Wear sun-protective clothing. Most summer clothing doesn’t provide a measurable amount of sun protection, but there are clothes out there that are specifically designed to protect you from the sun. Sun-protective clothing will have a UPF rating that measures how much protection it offers. Look for something with a UPF rating of at least 30, and make sure to wear long sleeves, long pants, and high collars to protect the most amount of skin. For regular clothes that aren't UPF rated, dark clothes with a tight weave will provide more protection than light colors and open weaves.

Cover your face. To protect your face from tanning or burning, wear a wide-brimmed hat with a brim that’s at least two to three inches wide. Be wary of straw hats and hats with open weaves that still allow the sun through. Look for hats with total coverage brims or veils that protect sensitive areas like the ears and back of the neck. If you want to wear a baseball hat or hat with minimal coverage, pair it with a sun-protective veil or bandana that will cover exposed areas.
Beware of reflected sunlight. Sunlight and UV rays reflect off a wide number of surfaces. You have to be careful of the rays from the sky and the ones bouncing back at you from below, because they can all darken your skin. Some of the most reflective surfaces are water, snow, sand, and concrete.
Preventing Skin Darkening Through Diet
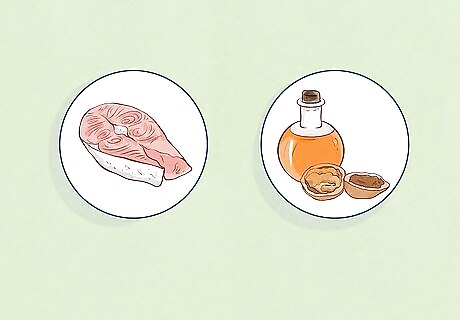
Eat foods that are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. There is growing evidence suggesting that a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids can help protect the skin from the sun. However, it’s important to use diet in conjunction with other sun-protection measures, such as using sunscreen and wearing protective clothes. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids include: Salmon Halibut Algae Nut oils Chia and hemp seeds
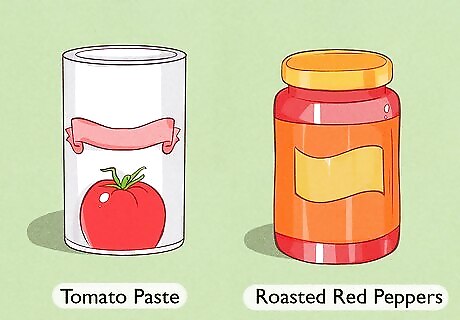
Add lycopene-rich foods to your dinners. Lycopene is an antioxidant that’s found primarily in red foods such as tomatoes and red peppers. However, in order to attain the most sun-protection benefits from lycopene, it’s important to cook the foods in a small amount of oil. Good sources of lycopene, therefore, include: Tomato paste Vegetable pasta sauces Roasted red peppers

Eat dark chocolate. Cocoa is packed with antioxidants such as flavonoids and catechins, and eating it can help your skin protect itself from sun damage. To get the most benefits from dark chocolate, eat about 2 oz (60 g) per day. Avoid chocolate that has milk added to it, as this can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb all antioxidants.
Avoiding the Sun
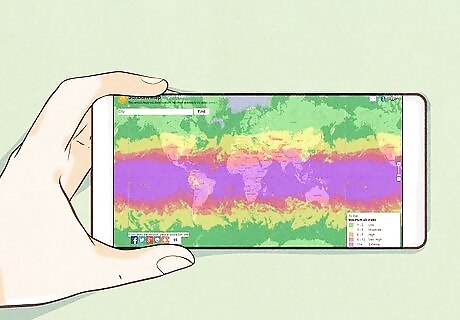
Keep an eye on the UV index. The UV index is a measure of the strength of the sun’s UVA and UVB rays on any given day. The higher the index the stronger the sun, and the greater chance there is of tanning and damaging your skin. You can check the UV index in your area on local weather reports, or websites like the Sunburn Map, and the World Health Organization’s UV Index webpage. A low UV index is between 0 and 2, and indicates that you don’t really have to worry about sun protection. A moderate UV index is between 3 and 7, and this means sun protection is required. A high UV index is 8 and above, and means that you should take extreme precautions to protect yourself. An extremely high UV index is 10 and over. When the sun is this strong, you should stay indoors whenever possible.

Stay out of the sun when it’s strongest. The sun is always strongest between the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. When possible, you should stay indoors during this time. To avoid the sun during peak times, try to schedule outdoor activities and trips for the early morning or late afternoon instead of midday. It’s not always possible to stay inside when the sun’s rays are at their most intense, but if you must go out, take precautions to protect your skin. This is especially true when the UV index is moderate or high. The sun is stronger in the summer months, but you do still have to worry about sun protection in the winter. This is especially true if you like to ski, for instance, because the air is thinner at higher altitudes, and this means the sun is stronger.

Seek shade. When you do have to be outside in the sun, staying in the shade is one of the best ways to protect yourself from your skin getting darker. Finding shade is especially important on high index days, and when the sun is at its strongest in the middle of the day. Great sources of shade include: Tall trees with dense leaves Buildings Roofed structures like gazebos and patios

Make your own shade. It’s always a good idea to take a regular umbrella out with you, because it can protect you against both sun and rain. A black umbrella can provide a UPF of 50+, so you can use an umbrella to create shade for yourself when you have to be out in the sun. Be careful, however, that you are still wearing sunscreen and protective clothing under the umbrella, because UV will still reflect off a number of surfaces. The larger the umbrella the better, because a bigger umbrella will protect you from more reflected UV.



















Comments
0 comment