views
X
Research source
Cleaning Minor Bites at Home
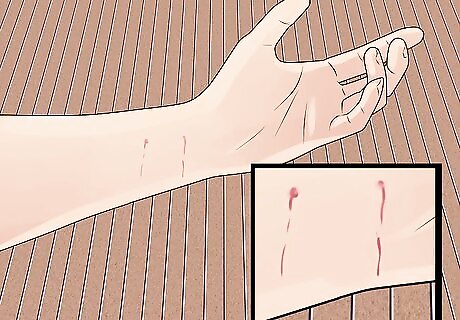
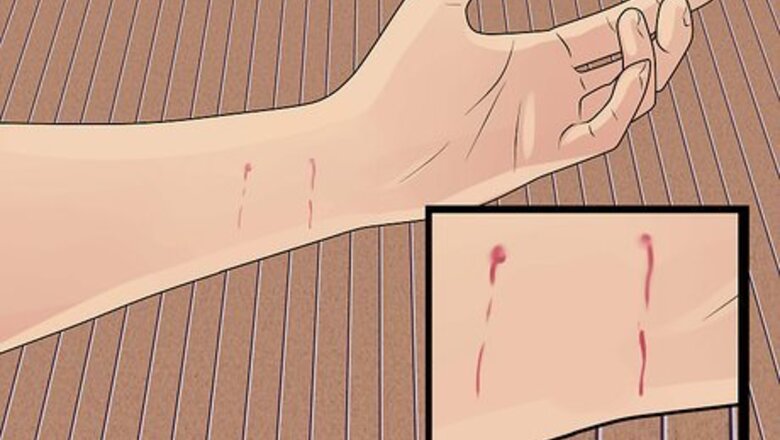
Assess the severity of the bite. Sometimes cats just give warning nips without breaking the skin, other times the bites can result in deep punctures from their fangs. Inspect the bite and look for areas where the skin may have been broken. A child may be crying and scared, even if the bite did not break the skin.
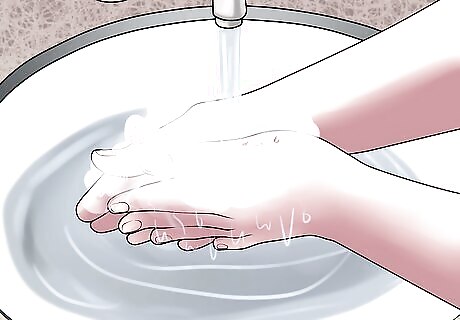
Wash a minor bite. If the cat’s teeth did not break the skin or broke the skin but did not go deep, you can wash and clean the bite at home. Thoroughly wash the bite with soap and clean tap water, allowing the water to flow over the bite and remove dirt and bacteria from the wound. Hold the bite under running water for several minutes. Gently squeeze the bite to help the blood flow. This will help remove dirt and bacteria from the inside of the wound.
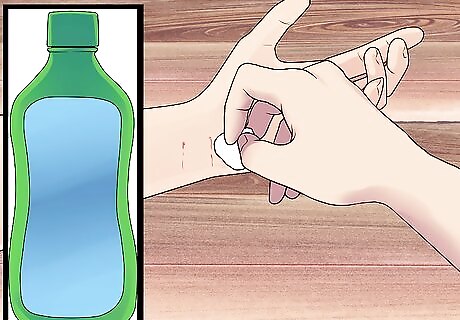
Disinfect the wound to prevent bacteria or other pathogens from growing. Put the disinfectant on a sterile cotton ball and then gently wipe it over the bite. It will probably sting, but only briefly. The following chemicals have excellent germicidal properties: Rubbing alcohol Iodine scrub Hydrogen peroxide
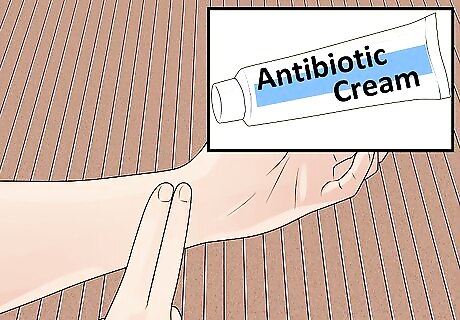
Prevent infection in a minor bite by applying an over-the-counter antibiotic cream. Smear a pea-sized amount of topical antibiotic cream over all areas where the skin was broken. Triple antibiotic creams are widely available and effective. Always read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions. Talk to a doctor before using these medications on infants or if you are pregnant.
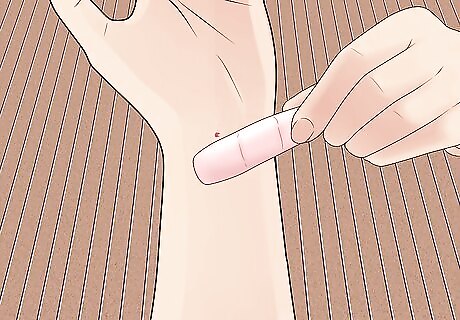
Protect the wound with a band aid. This will help keep dirt and bacteria out as it heals. Cover all areas where the skin was broken with a clean band aid. Because cat bites usually cover a small area, you will probably be able to cover it with an over-the-counter adhesive Band Aid. Dry the bite first, to help the Band Aid stick.
Seek Medical Care for Severe Bites
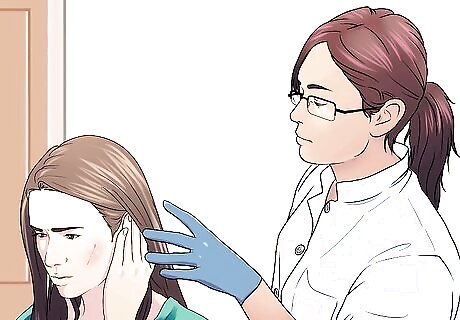
Go to the doctor if your bite is too serious for you to care for it adequately. This includes bites that: Are on the face Have deep puncture wounds from the cat’s fangs Bleed a lot and won’t stop Have damaged tissue that needs to be removed Are on joints, ligaments, or tendons

Discuss your treatment options with your doctor. Depending upon your particular bite and health condition, your doctor may: Close wounds to stop bleeding Remove dead tissue to prevent infection Do X-rays to assess damage to joints Recommend reconstructive surgery if you have severe damage or risk of scars

Take antibiotics if your doctor prescribes them. This can help reduce your chances of getting an infection. They are frequently prescribed for severe cat bites, particularly for people who are have weakened immune systems from conditions like diabetes or HIV or are undergoing chemotherapy. Your doctor may prescribe: Cefalexin Doxycycline Co-Amoxiclav Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride Metronidazole
Determining the Risk of Disease Transmission
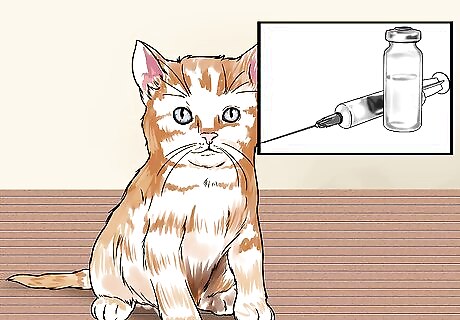
Determine the cat’s immunization status. Unvaccinated cats may be infected with diseases that can be transmitted through bites and are dangerous for people. If the cat is a pet, consult the owner about whether the cat is up-to-date on its shots. If the cat is yours, check your records to see when it was last vaccinated. Go to the doctor immediately if the cat is wild, feral, or you can’t confirm that it was up-to-date on its shots. Even if the cat looked healthy, you should still go to the doctor if you can't confirm that the cat had its shots. The cat could still have been carrying a disease, but just not have been symptomatic.
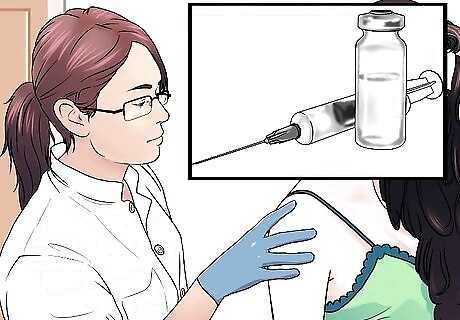
Get vaccinated if necessary. People who have been bitten by cats are at risk for several diseases. Your doctor may recommend you be vaccinated for: Rabies. While some animals with rabies may be clearly ill, including the classic symptom of foaming at the mouth, the disease can be transmitted before the symptoms become obvious. If there is a chance you were infected with rabies, the doctor will vaccinate you against the infection. Tetanus. Tetanus is caused by a bacteria that is in dirt and animal feces. This means that if your wound looks dirty or deep, and you haven’t had a tetanus shot within the last five years, your doctor may give you one to be sure that you won’t get infected.
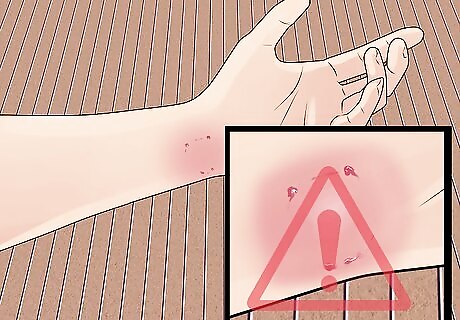
Monitor the wound for signs of infection. Go to the doctor immediately if you have any of the following signs of infection: Redness Swelling Increasing pain over time Pus or fluid coming from the wound Swollen lymph nodes Fever Chills and shivering
Preventing Cat Bites
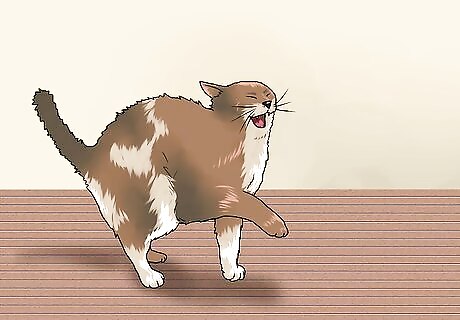
Learn how to recognize when cats are feeling threatened. Most cat bites occur when cats feel that they have to defend themselves. If you have pet cats, teach your children to understand your cats' body language. A cat that is scared may: Hiss Growl Lay his ears flat against his head Become pilo erect, in which the fur stands up, making the cat look bigger than usual

Be gentle to cats. Frequent situations in which a cat may become aggressive include: When she is cornered If her tail is pulled If she is held when she is struggling to get away If she is startled or hurt During rough play. Instead of allowing your cat to wrestle with your hands or feet, drag a string and let the cat chase that instead.

Avoid interacting with stray cats. Strays often live in cities or towns, but they may not be used to close contact with humans. Don’t try to pet them or pick them up. Don't feed stray or feral cats in areas where they will come into contact with children. Cats that are not used to people may react unpredictably.



















Comments
0 comment