views
Distinguishing Between Male and Female American Robins
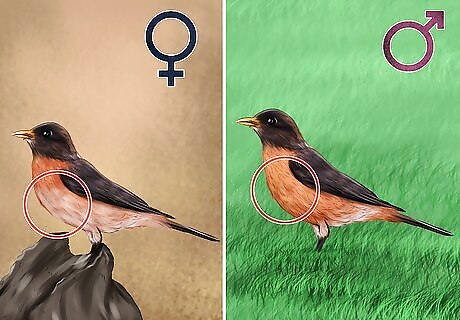
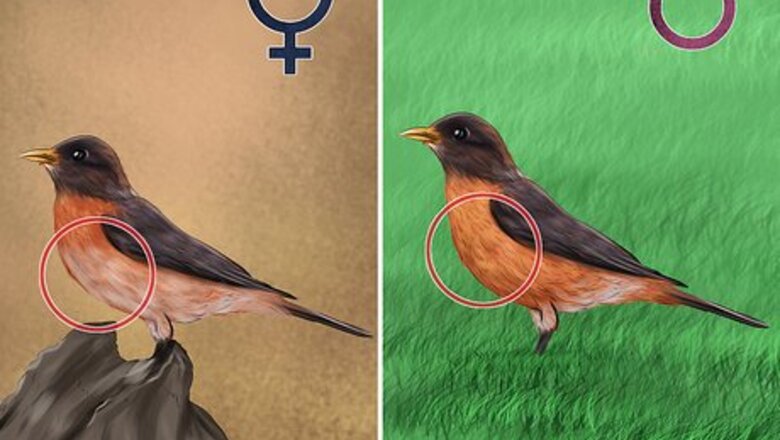
Study the robin’s plumage. The breast on male robins is a rusty red, deeper than that of their female counterparts. The female breast will be lighter in color, trending towards reddish-orange. Wing and tail feathers will also be different. Male robins tend to have darker black wings and tail feathers while females typically have a charcoal tone to their plumage. There is less contrast between the head and back feathers in females (where they are typically a blackish gray color) than among males.

Discover which bird is building the nest. Nests are built primarily by females. Male robins assist the building effort only occasionally. If you can catch a robin in the act of building its nest, chances are you've identified a female.

Observe nesting behavior. Male robins will care for the young at night during their first year. Female robins use this time to incubate the second brood but return during the day to feed and care for the hatchlings.

Pay attention to mating behavior. Males pursue females and may engage in fights with other males to ward them off their nesting grounds. Males often sing to attract females, though both males and females are capable of vocalizing.
Distinguishing Between Male and Female Australian (Scarlet) Robins

Look for differences in color. Male and female scarlet robins differ in their plumage significantly more than their European or American counterparts. Males are black with prominent bright red breasts and a white patch above the bill (frontal patch). Females, on the other hand, are brown with a rusty reddish-orange breast and white underparts.

Pay attention to nest behavior. Females sit on the eggs to incubate them. Males, on the other hand, provide their mates with food. This arrangement ensures the eggs stay warm and safe until they are ready to hatch.
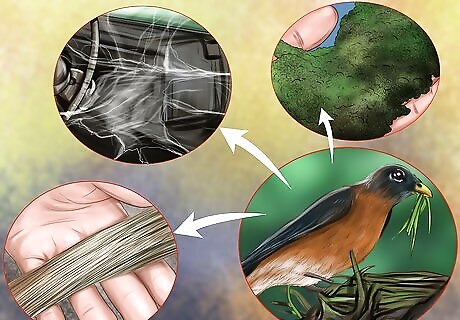
Observe how nesting grounds are established. Female scarlet robins build the actual nests with moss, spider webbing, and animal fibers. Males declare a nesting ground off-limits to other birds by vocalizing from a nearby lookout branch.
Distinguishing Between Male and Female European Robins
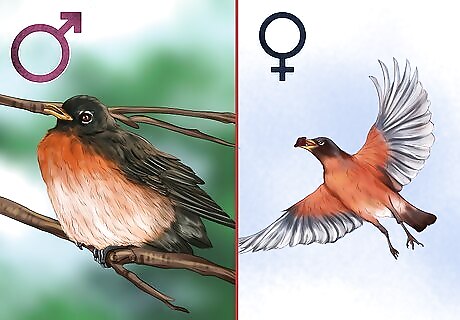
Follow migration patterns. Female robins will move to an adjacent nesting territory during the summer. Male robins, by contrast, remain on the same territory year-round.

Pay attention to mating behavior. Male robins bring females food -- seeds, worms, or berries -- in order to strengthen the mating bond. The female will warble noisily and flap her wings to communicate that she desires the male's gift.

Observe nesting behavior. After the female has laid eggs, she will remain in the nest for up to two weeks. During this time, the male will bring food to her and her young. If you see two robins in a nest with hatchlings and one flies away to obtain food, the one left in the nest is likely the female.

Examine the robin's breast. It is very difficult to distinguish between male and female robins using plumage. However, there are some subtle differences in the breasts of older robins. In male robins in their second year of life, the gray fringe around the red breast, continues to widen. The breast itself tends to be larger than that of females. While the fringe around the breast of the female robins does not widen significantly as they age, the female's red breast itself does continue to grow with age. Knowing the robin's age is important when utilizing breast characteristics to determine the sex of European robins.




















Comments
0 comment